How Does A Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer Work
Ronan Farrow
Apr 04, 2025 · 3 min read
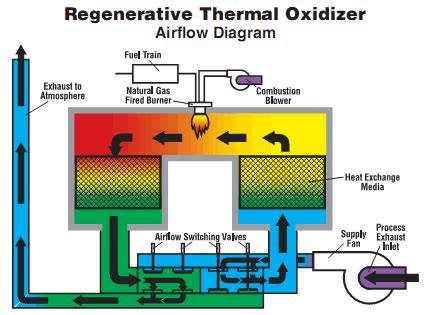
Table of Contents
How Does a Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO) Work? A Deep Dive into Emission Control
Regenerative thermal oxidizers (RTOs) are highly efficient systems used to control volatile organic compound (VOC) and other harmful emissions. They're increasingly popular due to their ability to achieve high destruction removal efficiency (DRE) while recovering a significant portion of the heat generated during the oxidation process. Understanding how they work is key to appreciating their effectiveness and choosing the right system for your specific application.
The Core Principle: Heat Recovery and Oxidation
At the heart of an RTO's functionality lies the principle of heat recovery. Unlike other oxidation systems that continuously vent a large amount of heat, RTOs cleverly capture and reuse this heat, significantly reducing energy consumption. This is achieved through a sophisticated system of ceramic media beds.
The Three-Bed System (Most Common)
The most common RTO configuration uses three ceramic media beds:
- Bed 1 (Heating): Contaminated air enters this bed, preheating as it passes through the hot ceramic media. The heated air then flows into the combustion chamber.
- Bed 2 (Combustion): The preheated air is oxidized in a combustion chamber at temperatures typically ranging from 700°C to 800°C (1300°F to 1470°F). This high temperature breaks down VOCs and other pollutants into carbon dioxide and water vapor.
- Bed 3 (Cooling): The cleaned, hot air flows through the third bed, transferring its heat to the ceramic media. This heat is then used to preheat the incoming contaminated air in Bed 1, completing the cycle.
The Two-Bed System
While less common, a two-bed system also exists. This design alternates between the two beds, with one bed heating while the other cools and vice-versa. Although slightly less energy-efficient than the three-bed system, it still offers significant cost savings compared to other oxidation methods.
The Regenerative Cycle: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The process is cyclical, continuously repeating to maintain efficient operation:
- Preheating: Contaminated air enters the system and passes through a bed of hot ceramic media, significantly raising its temperature.
- Oxidation: The preheated air then flows into the combustion chamber where the VOCs are oxidized at high temperatures. The combustion process requires a spark ignition, typically using natural gas as a supplemental fuel.
- Heat Recovery: After combustion, the hot, cleaned air passes through another bed of ceramic media, transferring its heat to the media.
- Switching Valves: A sophisticated valving system automatically switches the airflow between the beds, ensuring continuous operation and optimal heat recovery.
Benefits of Using an RTO
RTOs offer several key advantages over other emission control technologies:
- High DRE: Typically achieving a DRE of 95% or higher, ensuring effective pollutant destruction.
- Significant Energy Savings: The heat recovery system drastically reduces energy consumption compared to direct-fired thermal oxidizers.
- Lower Operating Costs: Reduced energy use translates to lower operating costs over the system's lifespan.
- Reduced Emissions: Effectively minimizes greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable operation.
- Versatile Application: Suitable for a wide range of industrial processes and applications.
Choosing the Right RTO
Selecting the appropriate RTO involves considering several factors, including:
- Airflow rate: The volume of air needing treatment.
- VOC concentration: The level of pollutants present in the air stream.
- Type of VOCs: The specific types of VOCs being oxidized.
- Operating temperature requirements: The necessary temperature for complete oxidation.
By understanding how a regenerative thermal oxidizer works, you can better appreciate its efficiency and its important role in reducing harmful emissions across diverse industries. Careful consideration of your specific needs is crucial when selecting the right RTO for optimal performance and long-term cost-effectiveness.
Featured Posts
Also read the following articles
| Article Title | Date |
|---|---|
| How Great Though Art Sheet Music | Apr 04, 2025 |
| How Hot Does A Harley Engine Get | Apr 04, 2025 |
| How Do Radio Stations Get Their Music | Apr 04, 2025 |
| How Do I Find The Flattest Route On Google Maps | Apr 04, 2025 |
| How Is Ashley Madison Legal | Apr 04, 2025 |
Latest Posts
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does A Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer Work . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
